- The process of collecting outcomes needed to determine whether the training is effective or not.
- The time, money and effort spent on training actually made difference in the outcome is evaluated.
- Training effectiveness refers to the benefits that company and trainees receive from training.
- The evaluation design is collection of information including what, when, how, from whom in a time interval.
- Investing millions in training needs in analyzing the outcome from training whether it is loss or profit in terms of performance.
- Training and Human Resource outcome includes attitude, motivation, behaviour and human capital.
- Organizational performance outcome includes performance and productivity.
- Financial outcomes include profits and financial indicators.
FORMATIVE EVALUATION
The evaluation of training that takes place during program. It helps to ensure whether
The evaluation of training that takes place during program. It helps to ensure whether
- Program is well organised and runs smoothly.
- Trainees learn and satisfy with the program
- It ensures to provide information about the program and how to make it better.
- And involves in collecting Qualitative data (Data that includes opinion, beliefs and feelings)
- Pilot Testing refers to the process of previewing the training program with potential trainees and managers or customers. It is used as "Dress rehearsal" and changes are made before the program.
- The evaluation conducted to determine to which level trainees have changed after training and involves in collecting Quantitative data.
- Quantitative data is collected through tests, ratings of behavior or objective measures of performance such as volume of sales, accidents or patents.
- To identify the program strength and weakness, meet with objectives, Transfer of Training is occurs and program is satisfactory.
- Trainees most and least benefit from the program is evaluated.
- Financial benefits and the cost of the program is evaluated.
- Compare different training programs conducted and choose the best program.
- Compare the cost and benefits of training vs non training
- Assess whether content, organisation and administration of program contribute to learning.
OUTCOME OF TRAINING EVALUATION
To measure outcome from training specific framework is used. Dr. kirkpatrick's four level framework has certain advantages and disadvantages. Hence five level framework is framed.
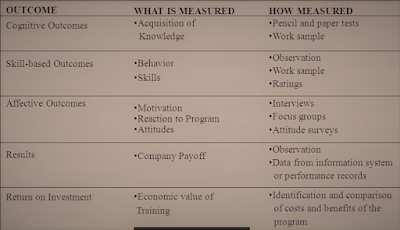
LEVEL 1 - Reaction Outcomes
LEVEL 2 - Learning and cognitive Outcomes
LEVEL 2 or 3 - Behavior or skill based Outcome
LEVEL 2 or 3 - Affective Outcomes
LEVEL 4 - Results
LEVEL 5 - Return on Investment
DETERMINING WHETHER OUTCOMES ARE APPROPRIATE
LEVEL 4 - Results
LEVEL 5 - Return on Investment
Training outcome is to be relevant, reliable, discrimination and practical.
Relevance is when learned capabilities measured relevant to what is performed by trainee.
Reliability is how frequently outcome is measured over time.
Discrimination is degree to which trainee performance on the outcome actually reflects true difference in performance.
Practicality is ease with which the outcome measures can be collected.